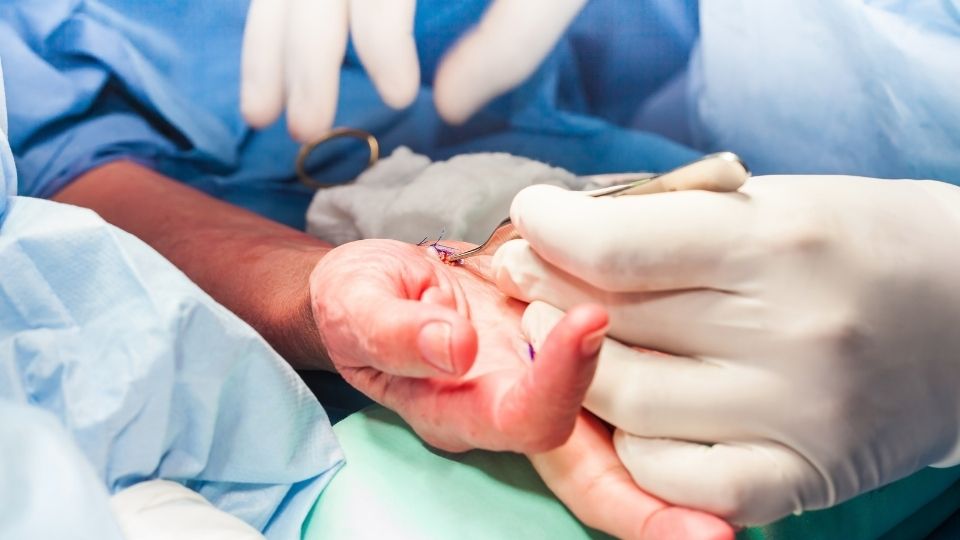
Hand surgery is a medical specialty that deals with diseases and injuries of the hand, wrist and forearm. Hands are one of the most complex structures in the human body and contain a complex set of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, nerves and vessels. Therefore, hand surgeons specialize in the diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of hand and wrist injuries, helping patients regain function and improve their quality of life.
Scope and Applications of Hand Surgery
Hand surgery addresses a number of different conditions, including fractures, dislocations, tendon injuries, nerve injuries, carpal tunnel syndrome, hand and wrist osteoarthritis, tendinitis, ganglion cysts, external junction tumors and reconstructive surgery. Hand surgeons offer surgical and non-surgical treatment options depending on the complexity of hand and wrist injuries. These include surgical repairs, tendon transplants, nerve reconstructions, joint prostheses, and rehabilitation methods such as physical therapy.
Diagnosis and Treatment Process
The diagnostic process of hand surgery involves many clinical evaluations. Physical examination, radiological imaging studies (x-rays, MRIs, CT scans), and sometimes neurological tests such as electromyography (EMG) help hand surgeons fully evaluate the patient's condition. The course of treatment is determined depending on the patient's condition and needs. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, while in other cases conservative treatment methods (e.g., immobilization, physical therapy, medications) may be sufficient.
Important Developments and Advances
Technological advances in hand surgery are constantly improving treatment options. Minimally invasive surgical techniques allow for smaller incisions and faster recovery times. Endoscopic methods enable hand surgeons to perform more precise and effective interventions. Additionally, reconstructive surgery techniques are used to heal hand and wrist injuries and achieve aesthetic results.